(p.s: code是真的短)
从头开始的详细版见WiKi
主要的难点都在后缀边和点的划分上。
重新声明一下定义:
我们按照这个字串在原串中每一个出现的最后一位的位置集合为一个点,即一个点里可以包含多个字串,我们钦定每个点中最长的字串长度为l e n i len_i l e n i
后缀边 按照点的集合定义,后缀边其实是把这些点按照集合包含关系连了起来(只会连所有包含关系中len最小的那个点),即成一棵树。
然后就好办了啊
建立SAM算法流程简析
首先建立前缀的节点,集合只有前缀本身
从上一个前缀节点开始向上搜索看有没有点有新加入字符的正向连边。(注意正向连边图是一个DAG)
分三种情况:
找到存在p,设q为p的该字符的对应点,
这个点继承q点后面一部分p+s
然后涉及到三个fa的更改:
1 fa[tot1]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot1;fa[ed]=tot1;
显然很好理解
接着我们要把所有从p往上跳的点(如果mp[p][s]是q)正向边全部改成新点即可。
大功告成
upd 2020/06/09
时隔4个月,发现自己并未理解完全理解SAM,于是趁停课的最后一天好好再理解&总结一遍。
我们定义
我们按照这个字串在原串中每一个出现的最后一位的位置集合(endpos)为一个点,即一个点里可以包含多个字串,我们钦定每个点中最长的字串长度为l e n i len_i l e n i
后缀边 按照点的集合定义,后缀边其实是把这些点按照集合包含关系连了起来(只会连所有包含关系中len最小的那个点),即成一棵树。
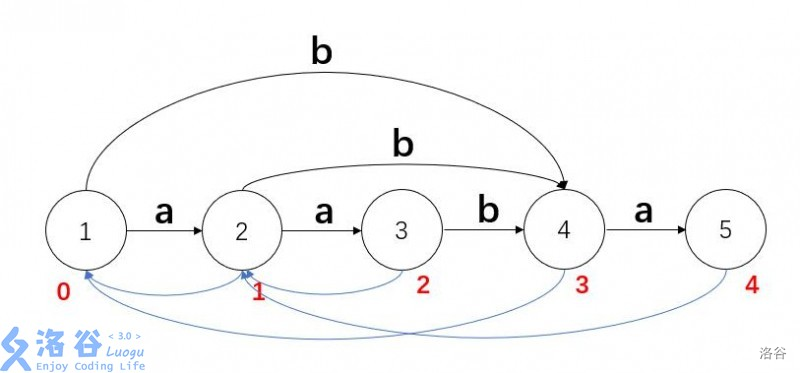
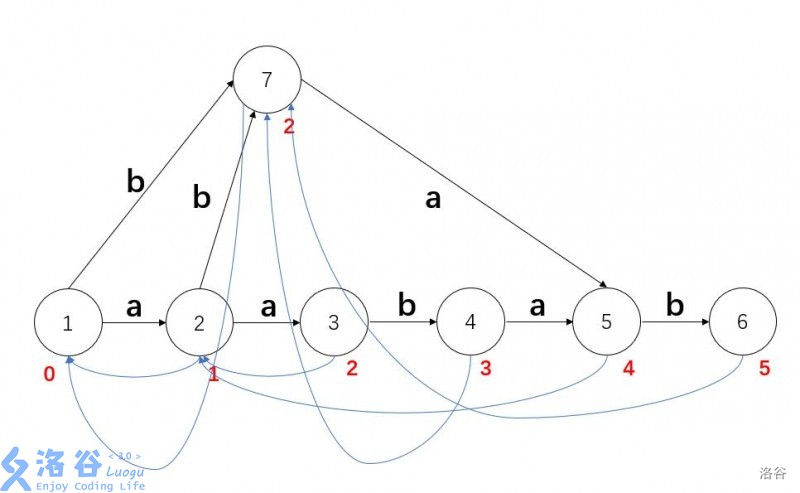
然后先看一下一颗标准的SAM的边和后缀边:
注意每一个节点表示endpos相同的所有子串的集合,图中仅标注集合中长度最大的子串。
然后记录一些关于最难理解的插入函数的一些思考:
部分参考:这篇博客
我们要做的事:注意一下,加入c后,endpos可能发生变化的字符串只有新串的后缀(或者说,旧串的后缀c)(它们无论在旧串出现与否,在新串中出现的次数一定会比在旧串中多1)。所以我们的任务就是处理好这些endpos发生变化的字符串(具体做法是遍历旧串后缀(事实上是遍历旧串的后缀自动机的终止节点),看看它们加c后endpos有没有改变)。还有,就是对于任意一个endpos变化的字符串,它的新endpos与原来endpos的差别只是多了一个n,即新串右端点的位置。因此我们判断一个串的endposs是否变化,只需要看其是否在新串最后出现即可。
由于len(fa(i))+1=minlen(i),因此对于i和fa(i),它们包含的子串的长度从大到小排序时也是连续的。所以我们把每一个节点想象成所有到达它的字符串的集合。那么,这个跳fa(i)的操作可以理解为压缩地遍历一个串的所有后缀。
关于 case 1
1 2 3 4 for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed;if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ; }
这样的做法显然是正确的,因为这些后缀加了c产生的新字符串不是旧串的子串,但是因为是旧串的后缀,加上c后必然能在新串最右端出现一次,所以它们也只能在右端点为新串加入字符c的位置出现一次。那么这些新字符串的endpos为n,等同于新串最长前缀的endpos。因此向np连边是正确的。
1 2 3 4 int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[p]+1 ==len[q]){ fa[ed]=q;return ; }
请过case1 p在第一个有c边的祖先停下了。先说明一下为什么不用继续往上跳fa,判断是否有c边了呢?因为显然,再往上跳,跳到的都是现在的p中字符串的后缀,且长度还更短,因此在它们的后面再加c形成的新字符串显然还是旧串的子串。所以p的祖先都有c的出边。
此时,我们将q设为p的c出边到达的节点。此时,我们将做一个非常有趣的判断:len(q)是否等于len§+1。这个判断是什么意思呢?因为longest§+c
另外,还是要说明一下为什么不用继续跳fa。p边的后缀连边,一定是p的后缀,因为p+c是新串后缀且其中maxlen的子串也是新串的后缀,所以所有属于p’+c的集合也是新串后缀,但是长度更小,向其后缀依然是之前的集合。也就是说只有第一个p才会影响新点的后缀连边。
case 3
1 2 3 4 tot1++;len[tot1]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=26 ;i++) mp[tot1][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[tot1]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot1;fa[ed]=tot1; for (;mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot1;
那么,len(q)>len§+1代表了什么呢?它代表了还有至少一个比longest§+c
我们新建一个节点nq,让endpos多出了n的字符串转移到此节点。
新建了一个节点,要考虑它的连边,fa与len。
先考虑len。由上文我们知道,长度大于len§+1的字符串都不可能是新串的后缀。并且,p有一条连到nq的边。因此,我们把len(nq)设为len§+1。
然后考虑出边。由于nq只是q拆出来的一个点,我们考虑直接用q的边。这样做显然是正确的,因为把nq从q拆出来只是因为nq的endpos与q不一样。但是,在q后和nq后加同样的字符,得到的字符串必然属于同一个类(首先,它们之间必然存在后缀关系且在旧串中属于一个类。又因为这个类中的串必定不是新串的后缀(否则就应该先被跳到),没有受到新加入字符的影响,所以在它们新串中还是同属一个类)。
现在我们来分析这错综复杂的fa关系该如何操作。
现在需要调整的点有三个:
n e w n o d e , q , n q newnode , q , nq n e w n o d e , q , n q
其中我们从q中分裂出nq的目的就是为了去迎合n e w n o d e newnode n e w n o d e f a [ n e w n o d e ] = n p fa[newnode]=np f a [ n e w n o d e ] = n p f a [ q ] = n q fa[q]=nq f a [ q ] = n q f a [ n q ] = f a [ q ] fa[nq]=fa[q] f a [ n q ] = f a [ q ]
大概就是这个效果:
那么,为什么当dian[p].ch[c]!=p时,可以不继续跳了呢?那是因为,这时dian[p].ch[c]的指向的点肯定是q的某个祖先(p变短了,并且longest(p’)+c
例题环节
过于板子,建好SAM,给每个前缀的点标记为1,按后缀树dfs,子树siz之和即为出现次数,所以用每个集合的出现次数乘以maxlen更新答案即可。
实现细节:一开始编号从2开始,把1定位源点,这样递归fa时递归到0就可以退出了。
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define ll long long const int M=3e6 ;int n,m;ll maxx=0 ;char s[M];struct SAM { int nex[M],ed,go[M],head[M],tot1,tot2,mp[M][30 ],fa[M],len[M]; ll siz[M]; SAM (){ed=tot1=1 ;} inline void ins (int c,int pos) int p=ed;tot1++;len[ed=tot1]=pos;siz[tot1]=1 ; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[p]+1 ==len[q]){ fa[ed]=q;return ; } tot1++;len[tot1]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=26 ;i++) mp[tot1][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[tot1]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot1;fa[ed]=tot1; for (;mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot1; } inline void add (int u,int v) nex[++tot2]=head[u];head[u]=tot2;go[tot2]=v; } inline void build () for (int i=2 ;i<=tot1;i++) add (fa[i],i); } inline void dfs (int u) for (int i=head[u];i;i=nex[i]){ int v=go[i];dfs (v); siz[u]+=siz[v]; } if (siz[u]>1 ) maxx=max (maxx,(ll)siz[u]*len[u]); } }sam; signed main () cin>>(s+1 );n=strlen (s+1 ); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) sam.ins (s[i]-'a' +1 ,i); sam.build ();sam.dfs (1 ); cout<<maxx<<endl; return 0 ; }
我们建立SAM,把所有mp的边连上,注意到这是一个简单无环图且所有从起点的路径对应一个字串,所以dp统计不同路径数即可。
(p.s 最近树统计写多了,这里是简单无环图,不保证每个点只被dfs一次,所以要加个记忆化,可能只有我这个菜鸡才会第一遍T飞吧、)
code
只用改几个小地方。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 inline void dfs (int u) siz[u]=1 ; for (int i=head[u];i;i=nex[i]){ int v=go[i]; if (vis[v]) siz[u]+=vis[v]; else { dfs (v);siz[u]+=siz[v]; } }vis[u]=siz[u]; } inline void build () for (int i=1 ;i<=tot1;i++) for (int j=1 ;j<=26 ;j++) if (mp[i][j]) addedge (i,mp[i][j]); } inline void print () cout<<siz[1 ]-1 <<endl; }
题目要求在线求解每加一个字符的所有不同子串的数量。
我们再例题2中学习到可以用原点的不同路径数表示不同子串。但是我们要随时维护路径数在加点改fa中,略显困难。
换一种思虑,想一想每个节点代表什么?是一类endpos相同的子串的集合。其中子串个数是m a x l e n [ x ] − m i n l e n [ x ] + 1 maxlen[x]-minlen[x]+1 m a x l e n [ x ] − m i n l e n [ x ] + 1 m a x l e n [ x ] − m a x l e n [ f a [ x ] ] maxlen[x]-maxlen[fa[x]] m a x l e n [ x ] − m a x l e n [ f a [ x ] ]
注意到新加一个字符时,真正权值有变化的点只有新加的endpos为pos的一个点(其它的点都是在之前的基础上分裂,不会对新子串有影响)。
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define int long long const int M=5e5 +5 ;int n,m,ans=0 ,cha[M];struct SAM { int ed,tot,fa[M],len[M]; map <int ,int > mp[M]; SAM (){ed=tot=1 ;} inline void Insert (int c,int pos) int p=ed;tot++;len[tot]=pos;ed=tot; for (;mp[p][c]==0 &&p;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;ans+=len[ed]-len[fa[ed]];return ; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[q]==len[p]+1 ){ fa[ed]=q;ans+=len[ed]-len[fa[ed]];return ; } int oldsum=len[q]-len[fa[q]]; len[++tot]=len[p]+1 ;mp[tot]=mp[q]; fa[ed]=tot;fa[tot]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot; ans+=len[ed]-len[fa[ed]]; } }sam; signed main () cin>>n; for (int i=1 ,x;i<=n;i++){ scanf ("%lld" ,&x);sam.Insert (x,i); cout<<ans<<"\n" ; } return 0 ; }
我们考虑在SAM上尝试查询第k大,首先对于SAM上每一个状态,我们预处理其单状态的出现次数(若不重复即为1,可重复即为endpos的数量(等于其被后缀链接的dfs边数))。
然后再预处理每个节点子树的数量之和,然后在SAM上每个节点按照a − z a-z a − z
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define ll long long const int M=2e6 +5 ;int op,tot1=1 ;int nex[M],head[M],len[M],go[M],fa[M],mp[M][30 ],ed=1 ,tot,vis[M],son[M],iso[M];ll siz[M],k; vector <int > g[M]; struct SAM { inline void Insert (int c,int pos) int p=ed;len[ed=++tot1]=pos;iso[ed]=1 ; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[q]==len[p]+1 ){ fa[ed]=q;return ; } tot1++;len[tot1]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++) mp[tot1][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[ed]=tot1;fa[tot1]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot1; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot1; } inline void add (int u,int v) nex[++tot]=head[u];head[u]=tot;go[tot]=v; } inline void build () for (int i=1 ;i<=tot1;i++) for (int j=0 ;j<26 ;j++) if (mp[i][j]) add (i,mp[i][j]); } void dfs (int u) for (int i=head[u];i;i=nex[i]){ int v=go[i];if (!vis[v]) dfs (v); siz[u]+=siz[v]; } vis[u]=1 ; } inline void Find (int pos,ll k) if (k<=0 ) return ; for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++){ if (!mp[pos][i]) continue ; int v=mp[pos][i]; if (siz[v]<k){ k-=siz[v];continue ; } cout<<(char )(i+'a' ); Find (v,k-iso[v]);break ; } } void dfsfa (int u) for (int i=0 ;i<g[u].size ();i++){ int v=g[u][i];dfsfa (v); iso[u]+=iso[v]; } } inline void buildfa () for (int i=2 ;i<=tot1;i++) g[fa[i]].push_back (i); dfsfa (1 ); } }sam; signed main () string s;cin>>s>>op>>k; int len=s.size (); for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ sam.Insert (s[i]-'a' ,i+1 ); } sam.build (); if (op==0 ) for (int i=1 ;i<=tot1;i++) siz[i]=iso[i]=1 ; if (op==1 ){ sam.buildfa (); } for (int i=2 ;i<=tot1;i++) siz[i]=iso[i]; sam.dfs (1 );siz[1 ]--;iso[1 ]=1 ; if (siz[1 ]<k) cout<<-1 ;else sam.Find (1 ,k); return 0 ; }
建立S S S
如果有边,m x l e n + + mxlen++ m x l e n + + f a fa f a p o s pos p o s m x l e n mxlen m x l e n l e n [ f a ] len[fa] l e n [ f a ] m x l e n mxlen m x l e n
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int M=1000005 ;int n,m,ans;string s,t; struct SAM { int mp[M][27 ],tot,ed,fa[M],len[M]; SAM (){ed=tot=1 ;} inline void Insert (int c,int pos) int p=ed;ed=++tot;len[tot]=pos; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[p]+1 ==len[q]){ fa[ed]=q;return ; } ++tot;len[tot]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++) mp[tot][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[ed]=tot;fa[tot]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot; for (;mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot; } inline void calc () int mxlen=0 ,s=1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<t.size ();i++){ int c=t[i]-'a' ; if (mp[s][c]){ mxlen++;s=mp[s][c]; } else { for (;s&&!mp[s][c];s=fa[s]); if (!s) s=1 ,mxlen=0 ; else mxlen=len[s]+1 ,s=mp[s][c]; } ans=max (ans,mxlen); } } }sam; int main () cin>>s>>t; for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++) sam.Insert (s[i]-'a' ,i+1 ); sam.calc ();cout<<ans<<endl; return 0 ; }
是上一个问题的升级版。
我们同样对第一个串建立SAM,然后让每一个串都在其上跑两个串的LCS,同时记录在SAM上每一个节点的最大匹配值。
记录方法:和上一题不同,此题也要求出SAM上每一个节点的最长匹配,考虑dp,一个点的m x [ u ] = m i n ( l e n [ u ] , m a x ( m x [ v ] ) mx[u]=min(len[u],max(mx[v]) m x [ u ] = m i n ( l e n [ u ] , m a x ( m x [ v ] )
最后答案是所有最大匹配值最小值的最大值。
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int M=1000005 ;int n,m,ans,vis[M];string s[12 ]; struct SAM { int mp[M][27 ],etot,tot,ed,fa[M],len[M],mx[M],mi[M],nex[M],go[M],head[M]; SAM (){ed=tot=1 ;} inline void Insert (int c,int pos) int p=ed;ed=++tot;len[tot]=pos; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[p]+1 ==len[q]){ fa[ed]=q;return ; } ++tot;len[tot]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++) mp[tot][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[ed]=tot;fa[tot]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot; for (;mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot; } inline void calc (string t) int mxlen=0 ,s=1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<t.size ();i++){ int c=t[i]-'a' ; if (mp[s][c]){ mxlen++;s=mp[s][c]; } else { for (;s&&!mp[s][c];s=fa[s]); if (!s) s=1 ,mxlen=0 ; else mxlen=len[s]+1 ,s=mp[s][c]; } mx[s]=max (mx[s],mxlen); } } inline void Addedge (int u,int v) nex[++etot]=head[u];head[u]=etot;go[etot]=v; } void build () for (int i=2 ;i<=tot;i++)Addedge (fa[i],i); } void dfs (int u) for (int i=head[u];i;i=nex[i]){ int v=go[i];dfs (v); } if (mx[u]) mx[fa[u]]=max (mx[fa[u]],min (len[fa[u]],mx[u])); } }sam; int main () int cnt=1 ;while (cin>>s[cnt]) cnt++; n=cnt-1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s[1 ].size ();i++) sam.Insert (s[1 ][i]-'a' ,i+1 ); sam.build (); memset (sam.mi,0x3f ,sizeof (sam.mi)); for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i++){ memset (sam.mx,0 ,sizeof (sam.mx)); sam.calc (s[i]); sam.dfs (1 ); for (int j=1 ;j<=sam.tot;j++){ sam.mi[j]=min (sam.mi[j],sam.mx[j]); } } for (int i=1 ;i<=sam.tot;i++) ans=max (ans,sam.mi[i]); cout<<ans<<endl; return 0 ; }
我们要求每一个长度最多出现的次数。
我们注意后缀链接树上的一条链,从上往下出现次数单调递减,而出现的len的范围单增,同时因为长度为len-1的出现次数的一部分一定可以包含长度为len内,因而一个状态可以更新其最大len的次数及其< l e n <len < l e n
(p.s 算出每个状态的出现次数,叶子是每个状态单独出现的位置,即是字符串的len个前缀的状态。切忌不可简单的由是否有出度判断是否为叶子。)
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define int long long const int M=2e6 +1 ;int n,m,ed=1 ,tot=1 ,dp[M];struct SAM { int nex[M],head[M],go[M],mp[M][26 ],fa[M],etot,siz[M],len[M]; inline void Insert (int c,int pos) int p=ed;ed=++tot;len[ed]=pos;siz[tot]=1 ; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[q]==len[p]+1 ){ fa[ed]=q;return ; } ++tot;len[tot]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++) mp[tot][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[ed]=tot;fa[tot]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot; for (;mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot; } void Addedge (int u,int v) nex[++etot]=head[u];head[u]=etot;go[etot]=v; } void Build () for (int i=2 ;i<=tot;i++) Addedge (fa[i],i); } void dfs (int u) for (int i=head[u];i;i=nex[i]){ int v=go[i];dfs (v);siz[u]+=siz[v]; } dp[len[u]]=max (dp[len[u]],siz[u]); } }sam; string s; signed main () cin>>s;int len=s.size (); for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ sam.Insert (s[i]-'a' ,i+1 ); } sam.Build ();sam.dfs (1 ); for (int i=len;i>=1 ;i--) dp[i]=max (dp[i+1 ],dp[i]); for (int i=1 ;i<=len;i++) cout<<dp[i]<<"\n" ; return 0 ; }
用trie树解决公共部分,然后就按照trie树插入sam
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int M=2e6 +1 ;int n,m,pos[M];char s[M];struct Trie { int tr[M][26 ],tot,fa[M],c[M]; inline void Insert (char *s) int now=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<strlen (s);i++){ int ch=s[i]-'a' ; if (!tr[now][ch]) tr[now][ch]=++tot,fa[tot]=now,c[tot]=ch; now=tr[now][ch]; } } }Tr; struct SAM { int tot,ed,fa[M],mp[M][26 ],len[M]; SAM (){ed=tot=1 ;} inline int Insert (int c,int las) int p=las;ed=++tot;len[tot]=len[las]+1 ; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ed; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[q]==len[p]+1 ){ fa[ed]=q;return ed; } ++tot;len[tot]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++) mp[tot][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[ed]=tot;fa[tot]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot; return ed; } void bfs () pos[0 ]=1 ; queue<int >q;for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++) if (Tr.tr[0 ][i]) q.push (Tr.tr[0 ][i]); while (!q.empty ()){ int u=q.front ();q.pop (); pos[u]=Insert (Tr.c[u],pos[Tr.fa[u]]); for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++) if (Tr.tr[u][i]) q.push (Tr.tr[u][i]); } } void Solve () long long ans=0 ; for (int i=2 ;i<=tot;i++){ ans+=len[i]-len[fa[i]]; } cout<<ans<<endl; } }sam; signed main () cin>>n; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ scanf ("%s" ,s);Tr.Insert (s); } sam.bfs ();sam.Solve (); return 0 ; }
建立广义sam,对每一个串的节点算出长度和出现次数,对于sam上每一个节点贡献就是l e n ∗ ( r i g h t 1 ∗ r i g h t 2 ) len*(right_1*right_2) l e n ∗ ( r i g h t 1 ∗ r i g h t 2 )
例题10 [BJOI2015]隐身术
暴力dfs,用SAM可以O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 )
code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define int long long const int M=1e6 +5 ;int T,lens,lent,n,k,tot=1 ,ed=1 ,lg[M],re[M],minn[M][21 ],re1[M],re2[M],cnt[M];struct SAM { int mp[M][30 ],no,fa[M],len[M],etot,dep[M],head[M],nex[M],go[M],dfn[M],st[M]; void Insert (int c,int pos) int p=ed;ed=++tot;len[ed]=pos;re[pos]=ed; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==0 ;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=ed; if (!p){ fa[ed]=1 ;return ; } int q=mp[p][c]; if (len[q]==len[p]+1 ){ fa[ed]=q;return ; } ++tot;len[tot]=len[p]+1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<=26 ;i++) mp[tot][i]=mp[q][i]; fa[ed]=tot;fa[tot]=fa[q];fa[q]=tot; for (;p&&mp[p][c]==q;p=fa[p]) mp[p][c]=tot; } inline void Addedge (int u,int v) nex[++etot]=head[u];head[u]=etot;go[etot]=v; } void dfs (int u) dfn[++no]=u;st[u]=no; for (int i=head[u];i;i=nex[i]){ int v=go[i];dep[v]=dep[u]+1 ;dfs (v);dfn[++no]=u; } } inline void Build_G () for (int i=2 ;i<=tot;i++) Addedge (fa[i],i); dfs (1 ); } inline int Min (int x,int y) return dep[x]<dep[y]?x:y;} void Build_ST () for (int i=1 ;i<=no;i++) minn[i][0 ]=dfn[i]; for (int i=1 ;i<=lg[tot*2 ];i++) for (int j=1 ;j+(1 <<i)-1 <=tot*2 ;j++) minn[j][i]=Min (minn[j][i-1 ],minn[j+(1 <<(i-1 ))][i-1 ]); } inline int Getlca (int x,int y) if (st[x]>st[y]) swap (x,y); int l=st[x],r=st[y],k=lg[r-l+1 ]; return Min (minn[l][k],minn[r-(1 <<k)+1 ][k]); } inline int Lcp (int x,int y) return len[Getlca (x,y)];} }sam; void dfs (int x,int y,int z) if (z>k) return ; int lcp=sam.Lcp (re[re1[x]],re[re2[y]]); x+=lcp;y+=lcp; if (x==lens||y==lent){ int d=k-z-(lens-x); if (d<0 ) return ; int l=max ((int )0 ,y-T-d),r=min (lent-1 ,y-T+d); cnt[l]++;cnt[r+1 ]--;return ; } dfs (x+1 ,y+1 ,z+1 ); dfs (x+1 ,y,z+1 ); dfs (x,y+1 ,z+1 ); } string s,t; signed main () cin>>k>>s>>t; lens=s.size (),lent=t.size (); for (int i=0 ;i<lens;i++) re1[i]=lent+lens+1 -i; for (int i=0 ;i<lent;i++) re2[i]=lent-i; s=s+"#" ;s=s+t; for (int i=2 ;i<=1000000 ;i++) lg[i]=lg[i>>1 ]+1 ; int len=s.size (); for (int i=len-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){ if (s[i]=='#' ) sam.Insert (26 ,len-i); else sam.Insert (s[i]-'A' ,len-i); } sam.Build_G ();sam.Build_ST (); int L=max ((int )0 ,lens-k),R=min (lent,lens+k); int ans=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<lent;i++){ T=i; dfs (0 ,i,0 ); for (int i=L;i<=R;i++){ cnt[i]+=cnt[i-1 ]; } for (int i=L;i<=R;i++) if (cnt[i]) ans++,cnt[i]=0 ; } cout<<ans<<endl; return 0 ; }
 )
)